When it comes to anything anti-ageing, the first thing that comes to people’s minds is collagen! The global collagen market is expected to reach USD 16.7 billion by 2028, indicating that the demand for anti-ageing and rejuvenating products is enormous and will not slow down any time soon, making it a money-making machine!
Collagen is widely used in beauty and supplement industries, coming from fish or animals’ bones, skin, and connective tissue. It’s considered a by-product of the meat industry, which managed to turn the waste into gold.
Do collagen supplements work?
Most collagen brands claim to combat skin ageing and help with digestive issues and joint pains. But, what does science really have to say about collagen and these claims?
A 2022 research review published in Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care reported that, when paired with resistance training, collagen peptide supplementation may help promote connective tissue recovery, decrease pain, and improve strength and body composition.
One 2018 study conducted that in postmenopausal women, supplementing with specific collagen peptides (SCP) may be beneficial for bone health.
Also, some health practitioners say that collagen supplements can treat the leaky gut syndrome, also called intestinal permeability, although no scientific evidence supports this claim.
When it comes to skin health, human studies are lacking, but some randomised controlled trials have found that collagen supplements improve skin hydration and elasticity. However, it’s worth noticing that most available trials are fully or at least partially funded by supplement companies. This makes it tricky to determine how effective collagen supplements are and if they are worth their often hefty price.
So how do we stay “forever young” the evidence-based way – we support our own collagen production through diet and lifestyle!
Collagen is the most abundant protein in the human body. It’s like “the glue” holds your bones and muscles together. It is also found in the skin, responsible for its elasticity and strength. Your body can naturally make collagen by using protein, vitamin C, and other nutrients found in food.
Collagen is a very large protein made up of three chains of over 1000 amino acids each. However, we can only absorb small chains of amino acids called peptides. When we consume protein, whether it comes from an animal or plant, our digestive tract breaks down proteins into the building blocks (amino acids) for absorption and then rebuilds them into collagen within our bodies.
So if we don’t absorb collagen as is, why not focus on building blocks from healthful sources instead of spending money on supplements?
That could be because people often assume that plants don’t provide enough protein or have any. But, on the contrary, plant-based foods contain all the protein we need. (The graph below is proof of that.)
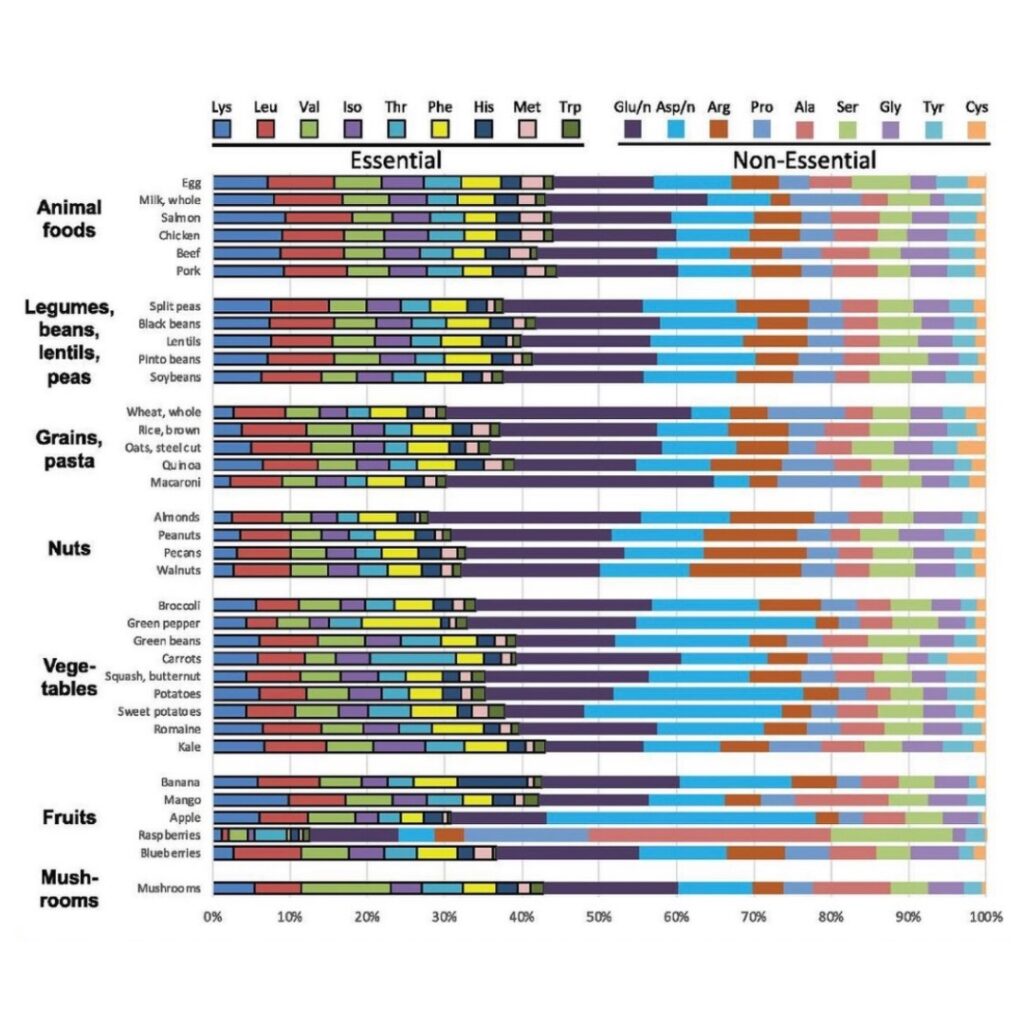
Essential amino acids are building blocks of protein that we must consume in our diets because we cannot produce them ourselves. The claim that plants don’t have protein or are incomplete has been going around for a long time and is often used by opponents of plant-based diets as proof that plants alone can’t provide enough protein to build muscles and support body health.
The truth is that all plant foods contain all of the essential amino acids in varying amounts. Some plant foods may contain lower amounts of specific amino acids, but as long as you eat a wide variety of whole foods, you won’t run into trouble.
At this point, you might wonder what do you need to do to help your body build and maintain collagen naturally? It’s simple- you need to focus on foods high in protein and skin-loving nutrients like vitamin C!
Glycine, proline and lysine are the specific three amino acids needed for creating collagen. You can find these amino acids in tofu, tempeh, edamame, beans, lentils, hemp, pumpkin, chia, sunflower seeds, mushrooms, asparagus, spirulina and leafy greens like watercress, spinach and turnip greens.
Vitamin C plays a crucial role in collagen synthesis and can be found only in plants! It protects the collagen you already have while supporting new collagen growth. Vitamin C is an essential cofactor for the two enzymes required for collagen synthesis: prolyl hydroxylase (to stabilize the collagen molecule) and lysyl hydroxylase (to give structural strength cross-linking). In addition, the research suggests that vitamin C acts directly on DNA, regulating and maintaining the intercellular amount of collagen.

Our collagen naturally decreases with age, so you must consume foods high in Vitamin C to prevent rapid skin ageing despite your source of protein. Excellent sources of vitamin C include citrus, bell pepper, broccoli, kale, Brussels sprouts, berries, pineapple, papaya, kiwi and fresh herbs.
Vitamin C is critical but not the only micronutrient required to sustain collagen production. Copper plays a significant role in collagen synthesis by activating an enzyme lysyl oxidase. Iron and Zinc also play an essential supporting role in the process, and their deficiencies can disrupt collagen synthesis. Good plant-based sources of these three minerals include tofu, tempeh, edamame, beans, lentils, nuts, seeds, leafy greens, whole grains, raisins, figs, avocado and dark chocolate.
Silicon is another trace element abundant in the human body and is vital for optimal collagen synthesis and activation of hydroxylating enzymes, improving skin strength and elasticity. We can consume silicon in the form of silica, or silicon dioxide, which can be found in green beans, leafy greens, lentils, brown rice, cereals and banana.
Vitamin A in the form of beta-carotene and Vitamin E are two nutrients with antioxidant properties, protecting skin against scavenging free radicals and collagen cross-linking. They also help maintain the skin barrier and protect the skin from ultraviolet radiation. Just like Vitamin C, they also stimulate collagen synthesis. They can be found in carrots, sweet potatoes, leafy greens, avocado, bell pepper, pumpkin, tomatoes, corn, mango, kiwi, papaya, apricots and watermelon.
Whole foods for the win
As you can see, plant-based foods provide all the protein and nutrients we need to build and protect collagen naturally. However, their significant advantage is that they are also high in phytonutrients that have consistently been shown to help fight against cellular damage and inflammation. For example, polyphenols like Catechins found in green tea protect the skin from ultraviolet radiation and suppress the age-related increase in collagen cross-linking. You can learn more about phytonutrients and antioxidants here.
To wrap it all up, I want to remind you that ageing is normal and you can’t stop the time or change your genetics. However, you can change how your body reads a DNA sequence.
Our lifestyle and food choices can switch genes on and off by regulating which genes are expressed in which parts of the body at any given time. For example, a pro-inflammatory diet high in sugar, saturated fats, alcohol, and processed foods can activate the genes that cause inflammation and damage collagen.
Diet plays a crucial role in maintaining a youthful appearance but don’t underestimate the power of lifestyle choices – prolonged sun exposure, smoking and stress cause collagen degradation in the skin, resulting in wrinkles and sagging. So the conclusion is to be mindful of your daily food choices and lifestyle activities if you want to age gracefully effortlessly!
References:
- Araújo LA, Addor F, Campos PM. Use of silicon for skin and hair care: an approach of chemical forms available and efficacy. An Bras Dermatol. 2016;91(3):331-335. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20163986
- Rutter K, Sell DR, Fraser N, et al. Green tea extract suppresses the age-related increase in collagen crosslinking and fluorescent products in C57BL/6 mice. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 2003;73(6):453-460. doi:10.1024/0300-9831.73.6.453
- Afaq F, Katiyar SK. Polyphenols: skin photoprotection and inhibition of photocarcinogenesis. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2011;11(14):1200-1215. doi:10.2174/13895575111091200
- Schagen SK, Zampeli VA, Makrantonaki E, Zouboulis CC. Discovering the link between nutrition and skin aging. Dermatoendocrinol. 2012;4(3):298-307. doi:10.4161/derm.22876
- Sang-Woon Choi, Simonetta Friso, Epigenetics: A New Bridge between Nutrition and Health, Advances in Nutrition, Volume 1, Issue 1, November 2010, Pages 8–16
